



Next: Communication with Other Elements
Up: Introducing Hsolve for Single
Previous: Interpreting the Mode of
Contents
The numerical advantage of implicit methods is that you can use a much
larger time step in order to compute the same neuronal model (this is
due to the stiffness of the system, see
[8]). In order to
examine the dependence of the results on the time step you can run a
simulation with and without hsolve while varying the time
step. However In this exercise we are concerned about something
completely different: hsolve optimizes the calculations such that it
runs faster than the original compartments. The speed advantage by
using hsolve is given in table
2.1.
Table:
Simulating a Purkinje cell containing 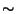 4000 compartments
without and with hsolve in
the different chanmodes.
The table lists two times three trials: the first set of
trials is done without any output. The second set is obtained
while plotting the membrane potential of the soma. All numbers
give the total CPU time needed to simulate 1000 steps, all
simulations used the same time step.
4000 compartments
without and with hsolve in
the different chanmodes.
The table lists two times three trials: the first set of
trials is done without any output. The second set is obtained
while plotting the membrane potential of the soma. All numbers
give the total CPU time needed to simulate 1000 steps, all
simulations used the same time step.
| no Xodus output |
| original |
66.30 |
66.44 |
66.41 |
| chanmode 0 |
56.79 |
56.76 |
56.81 |
| chanmode 1 |
40.26 |
40.27 |
40.34 |
| chanmode 2 |
15.45 |
15.27 |
15.31 |
| chanmode 3 |
14.02 |
13.90 |
13.90 |
| chanmode 4 |
16.47 |
15.96 |
16.05 |
| chanmode 5 |
16.99 |
16.55 |
16.49 |
Xodus output |
| original |
66.55 |
66.60 |
66.63 |
| chanmode 0 |
57.14 |
57.05 |
57.05 |
| chanmode 1 |
40.60 |
40.67 |
40.64 |
| chanmode 2 |
15.29 |
15.51 |
15.41 |
| chanmode 3 |
14.08 |
14.08 |
14.20 |
| chanmode 4 |
16.34 |
16.32 |
16.36 |
| chanmode 5 |
16.63 |
16.85 |
16.81 |
|




Next: Communication with Other Elements
Up: Introducing Hsolve for Single
Previous: Interpreting the Mode of
Contents
2002-11-15